- English
- 日本語
- 한국어
- Deutsch
- Français
- Español
No data
官方服务号
招聘公众号
免疫系统的核心在于精确调控自身抗原的识别与耐受,这是维护健康的关键。中枢耐受与外周耐受的双重机制共同确保了免疫系统的平衡。然而,当免疫系统受到“免疫预警信号”的挑战时,这种平衡可能受威胁,导致潜在的自身免疫性疾病(Autoimmune Disease, AID)风险。据统计,约有10%的健康人群血清中能检测到低水平的自身抗体,这些抗体虽未引发明显症状,却预示着免疫失衡的可能性。
“为更好生物医药”,ACROBiosystems百普赛斯与全球多家TOP药企建立了长期稳定合作,可提供覆盖早期研发、生产/质量控制、临床前/临床研究的重组蛋白、抗体、细胞株、试剂盒、类器官等产品及一站式服务在内的整体解决方案,为自身免疫疾病药物开发的快速推进提供有力支持。
| 早期研发 | 生产/质量控制 | 临床前/临床研究 |
|---|---|---|
|
靶点蛋白 100+自身免疫疾病靶点全覆盖 功能细胞株 TR-FRET试剂盒 抑制剂筛选试剂盒 分子互作分析检测服务(SPR&BLI) ... |
GMP级别生产原料 安全性指标检测试剂盒 残留检测试剂盒 ... |
类器官解决方案 抗独特型抗体及开发服务 ClinMax™细胞因子检测试剂盒 ... |
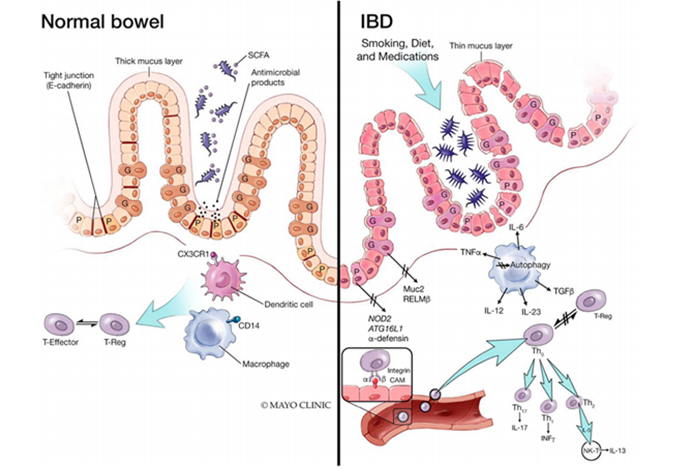
炎症性肠病的主要信号通路 [1]
炎症性肠病(Inflammatory Bowel Disease,IBD)是由免疫异常引发的慢性肠道炎症,包括克罗恩病和溃疡性结肠炎。其发病与免疫系统、肠道菌群及环境因素相互作用相关,异常激活的T/B细胞释放TNF-α、IL-17、TL1A等炎症因子,导致肠道组织损伤。核心免疫机制涉及Th17通路、JAK/STAT信号通路、TL1A/DR3通路及整合素介导的细胞黏附,这些通路的失调共同驱动了肠道持续炎症反应和病理进程。
1. Dunleavy KA, Raffals LE, Camilleri M. Intestinal barrier dysfunction in inflammatory bowel disease: underpinning pathogenesis and therapeutics. Digestive diseases and sciences. 2023, 68 (12):4306-20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-023-08122-w
2. Guo J, Zhang H, Lin W, et al. Signaling pathways and targeted therapies for psoriasis[J]. Signal transduction and targeted therapy, 2023, 8(1): 437. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-023-01655-6
3. Ding Q, Hu W, Wang R, et al. Signaling pathways in rheumatoid arthritis: implications for targeted therapy[J]. Signal transduction and targeted therapy, 2023, 8(1): 68. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-023-01331-9
4. Huang I H, Chung W H, Wu P C, et al. JAK–STAT signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis: An updated review[J]. Frontiers in immunology, 2022, 13: 1068260. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1068260
5. Podbielska M, O’Keeffe J, Pokryszko-Dragan A. New insights into multiple sclerosis mechanisms: lipids on the track to control inflammation and neurodegeneration[J]. International journal of molecular sciences, 2021, 22(14): 7319. https: //doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147319
6. Akhil A, Bansal R, Anupam K, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus: Latest insight into etiopathogenesis[J]. Rheumatology International, 2023, 43(8): 1381-1393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-023-05346-x
7. Zhang Y, Liu W, Lai J, et al. Genetic associations in ankylosing spondylitis: circulating proteins as drug targets and biomarkers[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2024, 15: 1394438. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1394438
8. Warshauer J T, Bluestone J A, Anderson M S. New frontiers in the treatment of type 1 diabetes[J]. Cell metabolism, 2020, 31(1): 46-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2019.11.017
9. Srivastava A, Makarenkova H P. Innate immunity and biological therapies for the treatment of Sjögren’s syndrome[J]. International journal of molecular sciences, 2020, 21(23): 9172. https: //doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239172
10. Iorio R. Myasthenia gravis: the changing treatment landscape in the era of molecular therapies[J]. Nature Reviews Neurology, 2024, 20(2): 84-98. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-023-00916-w