分子别名(Synonym)
AKT1,PKB,RAC,RAC-PK-alpha,PKB alpha
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Human Akt1, His,Strep II Tag (AK1-H5283) is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293). It contains AA Met 1 - Ala 480 (Accession # AAH00479).
Predicted N-terminus: Met
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus, followed by a twin strep tag. The protein has a calculated MW of 59.5 kDa. The protein migrates as 60-66 kDa under reducing (R) condition (SDS-PAGE) due to glycosylation.
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 1.0 EU per μg by the LAL method.
纯度(Purity)
>92% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in 20 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, pH8.0 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
电泳(SDS-PAGE)
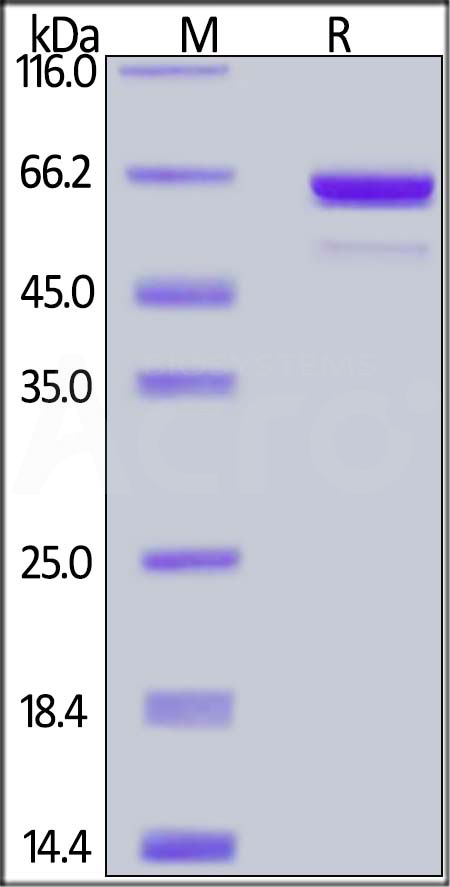
Human Akt1, His,Strep II Tag on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 92%.
背景(Background)
RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1) is also known PKB, Protein kinase B alpha, PKB alpha, Proto-oncogene c-Akt and RAC-PK-alpha, which belongs to the protein kinase superfamily, AGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family and RAC subfamily and is expressed in prostate cancer and levels increase from the normal to the malignant state (at protein level). AKT1 is one of 3 closely related serine/threonine-protein kinases (AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3) called the AKT kinase, and which regulate many processes including metabolism, proliferation, cell survival, growth and angiogenesis. AKT is responsible of the regulation of glucose uptake by mediating insulin-induced translocation of the SLC2A4/GLUT4 glucose transporter to the cell surface. AKT regulates also the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen by phosphorylating GSK3A at Ser-21 and GSK3B at Ser-9, resulting in inhibition of its kinase activity. Phosphorylation of GSK3 isoforms by AKT is also thought to be one mechanism by which cell proliferation is driven. AKT regulates also cell survival via the phosphorylation of MAP3K5 (apoptosis signal-related kinase).























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining













