分子别名(Synonym)
CD167a
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Mouse DDR1, Fc Tag (DD1-M5259) is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293). It contains AA Asp 22 - Thr 414 (Accession # Q03146-1).
Predicted N-terminus: Asp 22
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries a human IgG1 Fc tag at the C-terminus.
The protein has a calculated MW of 70.2 kDa. The protein migrates as 70-80 kDa under reducing (R) condition (SDS-PAGE) due to glycosylation.
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 1.0 EU per μg by the LAL method.
纯度(Purity)
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in 50 mM Tris,100 mM Glycine,25 mM Arginine,150 mM NaCl,pH7.5 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
电泳(SDS-PAGE)
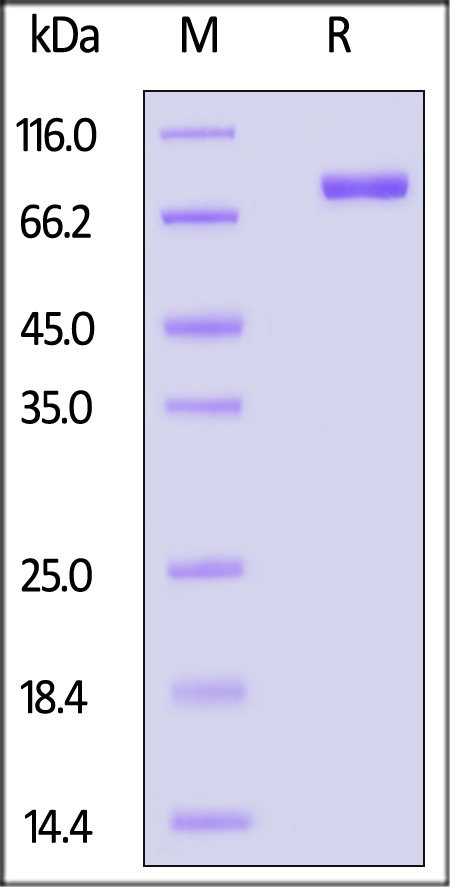

Mouse DDR1, Fc Tag on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 95%.
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
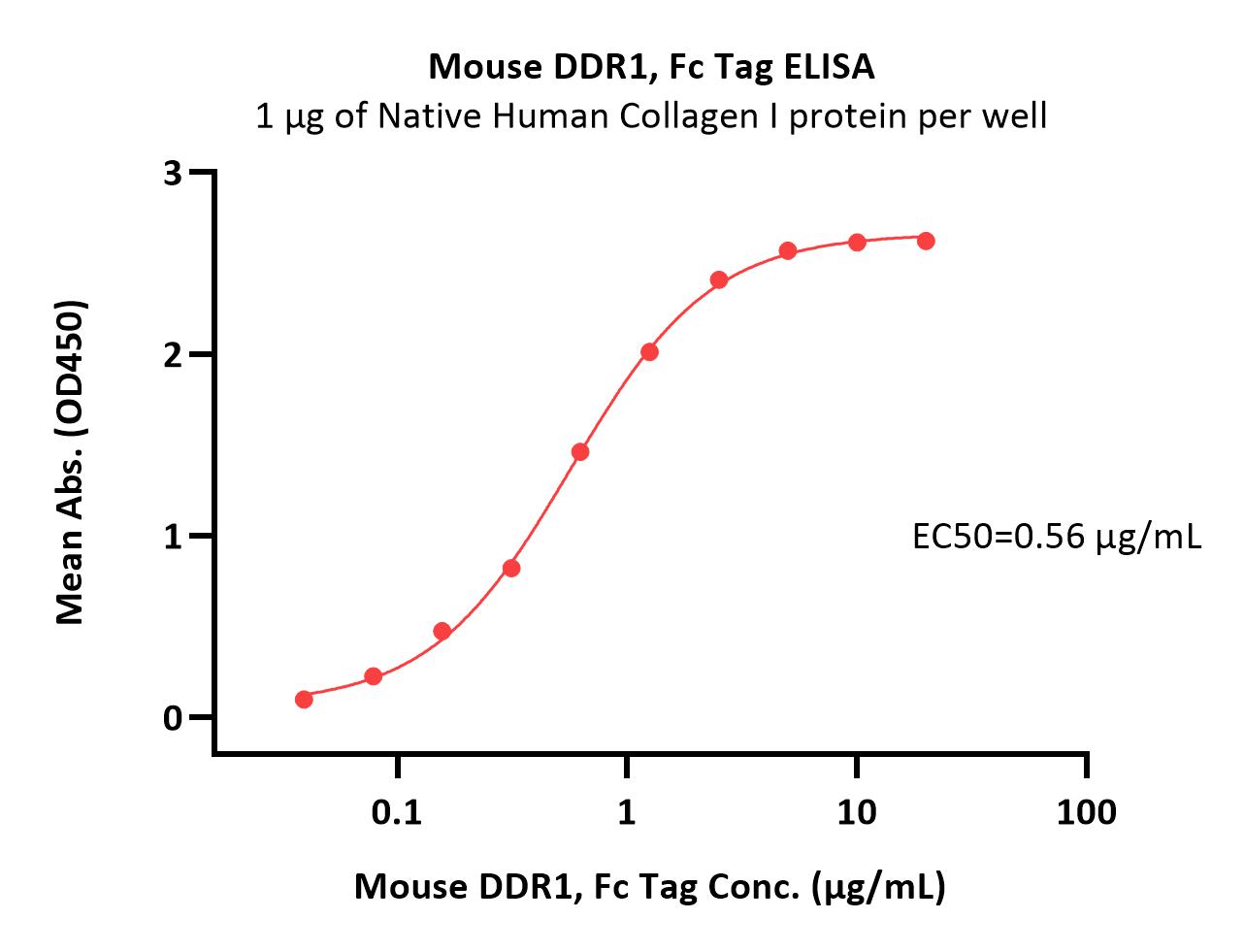
Immobilized Native Human Collagen I protein at 10 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Mouse DDR1, Fc Tag (Cat. No. DD1-M5259) with a linear range of 0.039-1.25 μg/mL (QC tested).
Protocol
背景(Background)
Discoidin domain receptor 1 (DDR1) is a member of DDRs, which are members of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK). Upon collagen binding, DDR1 undergoes tyrosine autophosphorylation, which consequently triggers downstream genetic and cellular pathways and plays critical roles in the regulation of cellular morphogenesis, differentiation, proliferation, adhesion, migration, and invasion. Research shows that DDR1 is closely related to various human diseases including cancer, fibrosis, atherosclerosis, and other inflammatory disorders. New generation DDR1 inhibitors targeting the allosteric sites outside of the canonical ATP-binding pocket or extracellular domain (allosteric inhibitors) may offer a new opportunity for selective DDR1 inhibition therapy development.






















































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining











