表达区间及表达系统(Source)
Nipah virus Post-Fusion glycoprotein, His Tag (PON-V52H3) is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293).
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)
This protein carries a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
The protein has a calculated MW of 54.5 kDa. The protein migrates as 55-60 kDa under reducing (R) condition (SDS-PAGE) due to glycosylation.
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 1.0 EU per μg by the LAL method / rFC method.
纯度(Purity)
>90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
>90% as determined by SEC-MALS.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in 0.1 M Sodium citrate, pH5.5 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
电泳(SDS-PAGE)
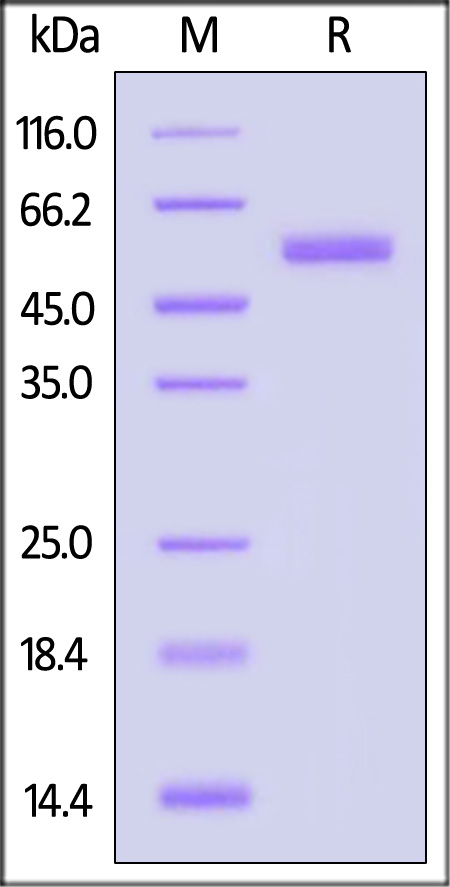

Nipah virus Post-Fusion glycoprotein, His Tag on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 90%.
SEC-MALS
The purity of Nipah virus Post-Fusion glycoprotein, His Tag (Cat. No. PON-V52H3) is more than 90% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 155-180 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
Report
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
Immobilized Nipah virus Pre-Fusion glycoprotein, His Tag (Cat. No. FUN-N52H3) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Anti-HeV/NiV F/Fusion glycoprotein F0 Antibody (5B3) with a linear range of 0.002-0.156 μg/mL. Nipah virus Post-Fusion glycoprotein, His Tag (Cat. No. PON-V52H3) is verified not recoginized by Anti-HeV/NiV F/Fusion glycoprotein F0 Antibody (5B3) (QC tested).
Protocol
背景(Background)
Hendra virus (HeV) and Nipah virus (NiV) are henipaviruses discovered in the mid-to late 1990s that possess a broad host tropism and are known to cause severe and often fatal disease in both humans and animals. HeV and NiV infect host cells through the coordinated efforts of two envelope glycoproteins. The G glycoprotein attaches to cell receptors, triggering the fusion (F) glycoprotein to execute membrane fusion. G is a type II homotetrameric transmembrane protein responsible for binding to ephrinB2 or ephrinB3 (ephrinB2/B3) receptors. F is a homotrimeric type I transmembrane protein that is synthesized as a premature F0 precursor and cleaved by cathepsin L during endocytic recycling to yield the mature, disulfide-linked, F1 and F2 subunits. Upon binding to ephrinB2/B3, NiV G undergoes conformational changes leading to F triggering and insertion of the F hydrophobic fusion peptide into the target membrane. Subsequent refolding into the more stable post-fusion F conformation drives merger of the viral and host membranes to form a pore for genome delivery to the cell cytoplasm.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining











