- Genetically modified cell lines best reflect MOA (Mechanism of Action)
- Higher activity and larger assay window for robust and reproducible cell-based bioassay
- Comprehensive application data to support assay development and validation
- Full tracible record, stringent quality control and validated cell passage stability
- Parental cell line legally obtained from internationally recognized cell resource bank and commercially licensed
- Global commercial license assistance whenever regulatory filing is required
描述(Description)
The CHO/Human c-MET Stable Cell Line was engineered to express the receptor full length human c-MET (Gene ID: 4233), used to mimic cancer target cells. Surface expression of human c-MET was confirmed by flow cytometry.
应用说明(Application)
• Useful for cell-based c-MET binding assay
生长特性(Growth Properties)
Adherent
筛选标记(Selection Marker)
Puromycin (2 μg/mL)
培养基(Complete Growth Medium)
F-12K + 10% FBS
冻存液(Freeze Medium)
Serum-free cell cryopreservation medium
装量(Quantity)
1 vial contains at least 5×10^6 cells in 1 mL serum-free cryopreservation medium
存储(Storage)
Frozen in liquid nitrogen.
支原体检测(Mycoplasma Testing)
Negative
无菌检测(Sterility Testing)
Negative
使用说明(Instructions for Use)
See data sheet for detailed culturing and assay protocol.
Receptor Assay
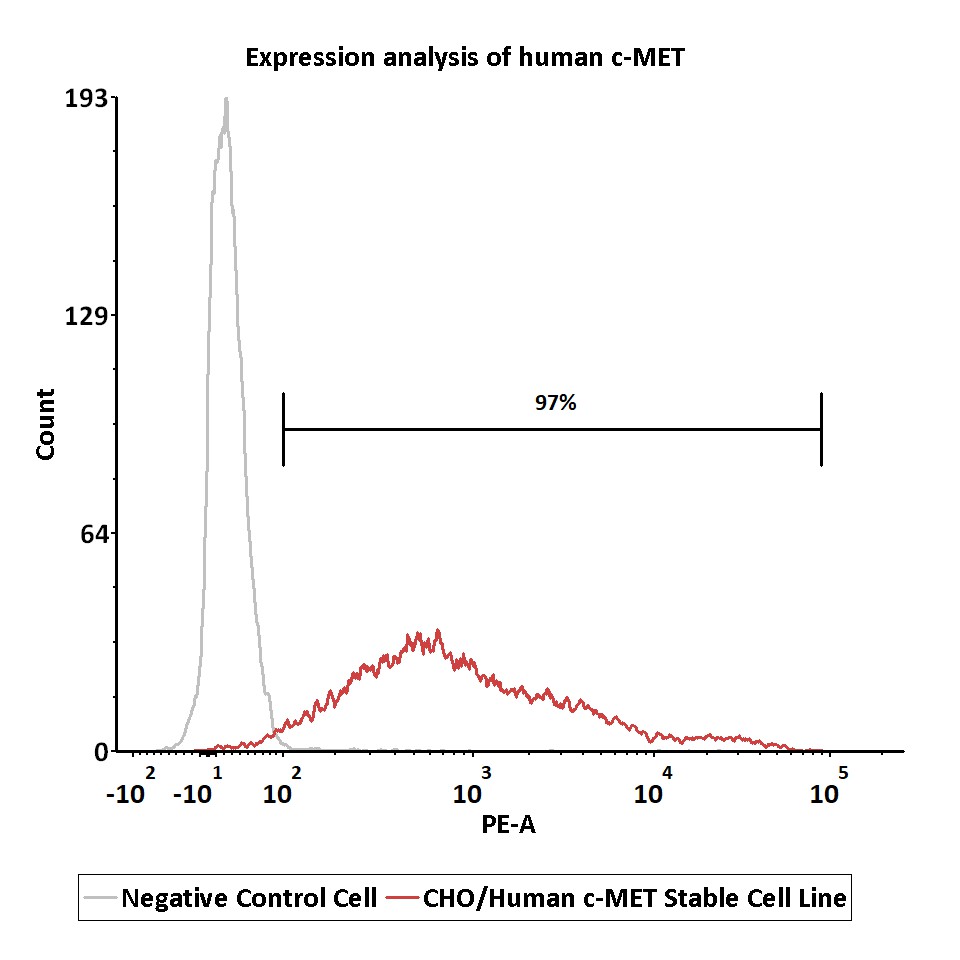
Expression analysis of human c-MET on CHO/Human c-MET Stable Cell Line by FACS.
Cell surface staining was performed on CHO/Human c-MET Stable Cell Line or negative control cell using PE-labeled anti-human c-MET antibody.
Protocol
如有相关细胞池需求请联系我们
背景(Background)
Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (HGFR) is also known as mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (MET), c-Met, and is a glycosylated receptor tyrosine kinase that plays a central role in epithelial morphogenesis and cancer development. HGFR protein possesses tyrosine-kinase activity. The primary single chain precursor protein is post-translationally cleaved to produce the alpha and beta subunits, which are disulfide linked to form the mature receptor. HGFR is normally expressed by cells of epithelial origin, while expression of HGF is restricted to cells of mesenchymal origin. Upon HGF stimulation, HGFR induces several biological responses that collectively give rise to a program known as invasive growth. Abnormal HGFR activation in cancer correlates with poor prognosis, where aberrantly active HGFR triggers tumor growth, formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) that supply the tumor with nutrients, and cancer spread to other organs (metastasis). HGFR is deregulated in many types of human malignancies, including cancers of kidney, liver, stomach, breast, and brain. Normally, only stem cells and progenitor cells express HGFR, However, cancer stem cells are thought to hijack the ability of normal stem cells to express HGFR, and thus become the cause of cancer persistence and spread to other sites in the body. Various mutations in the HGFR gene are associated with papillary renal carcinoma. HGFR mediates a complex program known as invasive growth. Activation of HGFR triggers mitogenesis, and morphogenesis.
Limited Use&License Disclosure
BY USE OF THIS PRODUCT, RESEARCHER AGREES TO BE BOUND BY THE FOLLOWING TERMS OF LIMITED USE OF THIS CELL LINE PRODUCT.
- If the researcher is not willing to accept the terms of limited use of this cell line product, and the product is unused, ACRO will accept return of the unused product.
- Researchers may use this product for research use only, no commercial use is allowed. "Commercial use" means any and all uses of this product and derivatives by a party for profit or other consideration and may include but is not limited to use in: (1) product manufacture; and (2) to provide a service, information or data; and/or resale of the product or its derivatives, whether or not such product or derivatives are resold for use in research.
- This cell line is neither intended for any animal or human therapeutic purposes nor for any direct human in vivo use . You have no right to share, modify, transfer, distribute, sell, sublicense, or otherwise make the cell line available for use to other researchers, laboratories, research institutions, hospitals, universities, or service organizations.
- ACROBIOSYSTEMS MAKES NO WARRANTIES OR REPRESENTATIONS OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, WITH RESPECT TO THE SUITABILITY OF THE CELL LINE FOR ANY PARTICULAR USE.
- ACROBIOSYSTEMS ACCEPTS NO LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH THE HANDLING OR USE OF THE CELL LINE.
- Modifications of the cell line, transfer to a third party, or commercial use of the cell line may require a separate license and additional fees. Please contact order.cn@acrobiosystems.com for further details.























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining











