Gene editing of CD3 epsilon to redirect regulatory T cells for adoptive T cell transferDu, Noyan, McCallion
et alMol Ther (2025) 33 (3), 997-1013
Abstract: Adoptive transfer of antigen-specific regulatory T cells (Tregs) is a promising strategy to combat immunopathologies in transplantation and autoimmune diseases. However, their low frequency in peripheral blood poses challenges for both manufacturing and clinical application. Chimeric antigen receptors have been used to redirect the specificity of Tregs, using retroviral vectors. However, retroviral gene transfer is costly, time consuming, and raises safety issues. Here, we explored non-viral CRISPR-Cas12a gene editing to redirect Tregs, using human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-A2-specific constructs for proof-of-concept studies in transplantation models. Knock-in of an antigen-binding domain into the N terminus of CD3 epsilon (CD3ε) gene generates Tregs expressing a chimeric CD3ε-T cell receptor fusion construct (TRuC) protein that integrates into the endogenous TCR/CD3 complex. These CD3ε-TRuC Tregs exhibit potent antigen-dependent activation while maintaining responsiveness to TCR/CD3 stimulation. This enables preferential enrichment of TRuC-redirected Tregs over CD3ε knockout Tregs via repetitive CD3/CD28 stimulation in a good manufacturing practice-compatible expansion system. CD3ε-TRuC Tregs retained their phenotypic, epigenetic, and functional identity. In a humanized mouse model, HLA-A2-specific CD3ε-TRuC Tregs demonstrate superior protection of allogeneic HLA-A2+ skin grafts from rejection compared with polyclonal Tregs. This approach provides a pathway for developing clinical-grade CD3ε-TRuC-based Treg cell products for transplantation immunotherapy and other immunopathologies.Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
A Bi-Specific T Cell-Engaging Antibody Shows Potent Activity, Specificity, and Tumor Microenvironment Remodeling in Experimental Syngeneic and Genetically Engineered Models of GBMZannikou, Duffy, Procissi
et albioRxiv (2025)
Abstract: Bispecific T cell-engagers (BTEs) are engineered antibodies that redirect T cells to target antigen-expressing tumors. BTEs targeting tumor-specific antigens such as interleukin 13 receptor alpha 2 (IL13Rα2) and EGFRvIII have been developed for glioblastoma (GBM). However, there is limited mechanistic understanding of the action of BTE since prior studies were mostly conducted in immunocompromised animal models. To close this gap, the function of BTEs was assessed in the immunosuppressive glioma microenvironment (TME) of orthotopic and genetically engineered mouse models (GEMM) with intact immune systems.A BTE that bridges CD3 epsilon on murine T cells to IL13Rα2-positive GBM cells was developed and the therapeutic mechanism investigated in immunocompetent mouse models of GBM. Multi-color flow cytometry, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-Seq), multiplex immunofluorescence, and multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) across multiple pre-clinical models of GBM were used to evaluate the mechanism and action and response.BTE-mediated interactions between murine T cells and GBM cells triggered T cell activation and antigen-dependent killing of GBM cells. BTE treatment significantly extended the survival of mice bearing IL13Rα2-expressing orthotopic glioma and de novo forming GBM in the GEMM. Quantified parametric MR imaging validated the survival data showing a reduction in glioma volume and decreased glioma viability. Flow cytometric and scRNA-seq analyses of the TME revealed robust increases in activated and memory T cells and decreases in immunosuppressive myeloid cells in the brains of mice following BTE treatment.Our data demonstrate that the survival benefits of BTEs in preclinical models of glioma are due to the ability to engage the host immune system in direct killing, induction of immunological memory, and modulation of the TME. These findings provide a deeper insight into the mechanism of BTE actions in GBM.
Characteristics and Significance of Tertiary Lymphoid Structures Based on Molecular Subtypes in Endometrial CancerJia, Zhang, Chen
et alInt J Gynecol Pathol (2024) 43 (6), 595-604
Abstract: The purpose of this study is to investigate the characteristics and significance of tertiary lymphoid structures (TLSs) in endometrial cancer (EC) based on molecular subtypes. A total of 220 patients with EC were retrospectively enrolled, including 20 with polymerase epsilon ultramutated (POLE-mut), 63 with mismatch repair deficient, 32 with p53 abnormal, and 105 with no specific molecular profile. The presence and maturity of TLSs were determined by immunohistochemical markers (CD3, CD20, CD21, and Bcl6). Disease-free survival served as the endpoint event. TLSs were found in 91 out of 220 patients (41.1%), with 68 located in peritumoral tissues and 37 exhibiting well-formed germinal center structures. The presence and different maturity of TLSs were closely associated with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and the programmed cell death ligand-1 expression. Moreover, TLSs displayed heterogeneity across different molecular subtypes. Notably, the TLSs, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, and expression of the programmed cell death ligand-1 were significantly enriched in POLE-mut EC. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed the presence of TLSs (odds ratio: 3.483, 95% CI: 1.044-11.623, P = 0.042) as a potential predictor of POLE-mut EC. Kaplan-Meier survival curves revealed that molecular subtypes significantly stratified prognosis in patients with EC (P = 0.002), whereas TLSs did not. Multivariate Cox regression analysis indicated that The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics stage and Ki-67 expression were independent prognostic factors affecting disease-free survival in patients with EC, and TLSs were not included. In conclusion, TLSs in EC exhibit heterogeneity based on molecular subtypes, necessitating further exploration to determine their clinical application value.Copyright © 2024 by the International Society of Gynecological Pathologists.
Exploitation of CD3ζ to enhance TCR expression levels and antigen-specific T cell functionDegirmencay, Thomas, Holler
et alFront Immunol (2024) 15, 1386132
Abstract: The expression levels of TCRs on the surface of human T cells define the avidity of TCR-HLA/peptide interactions. In this study, we have explored which components of the TCR-CD3 complex are involved in determining the surface expression levels of TCRs in primary human T cells. The results show that there is a surplus of endogenous TCR α/β chains that can be mobilised by providing T cells with additional CD3γ,δ,ε,ζ chains, which leads to a 5-fold increase in TCR α/β surface expression. The analysis of individual CD3 chains revealed that provision of additional ζ chain alone was sufficient to achieve a 3-fold increase in endogenous TCR expression. Similarly, CD3ζ also limits the expression levels of exogenous TCRs transduced into primary human T cells. Interestingly, transduction with TCR plus CD3ζ not only increased surface expression of the introduced TCR, but it also reduced mispairing with endogenous TCR chains, resulting in improved antigen-specific function. TCR reconstitution experiments in HEK293T cells that do not express endogenous TCR or CD3 showed that TCRα/β and all four CD3 chains were required for optimal surface expression, while in the absence of CD3ζ the TCR expression was reduced by 50%. Together, the data show that CD3ζ is a key regulator of TCR expression levels in human T cells, and that gene transfer of exogenous TCR plus CD3ζ improved TCR surface expression, reduced TCR mispairing and increased antigen-specific function.Copyright © 2024 Degirmencay, Thomas, Holler, Burgess, Morris and Stauss.
ISG15/GRAIL1/CD3 axis influences survival of patients with esophageal adenocarcinomaMcEwen, Ray, Nancarrow
et alJCI Insight (2024) 9 (13)
Abstract: Immunosuppression is a common feature of esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) and has been linked to poor overall survival (OS). We hypothesized that upstream factors might negatively influence CD3 levels and T cell activity, thus promoting immunosuppression and worse survival. We used clinical data and patient samples of those who progressed from Barrett's to dysplasia to EAC, investigated gene (RNA-Seq) and protein (tissue microarray) expression, and performed cell biology studies to delineate a pathway impacting CD3 protein stability that might influence EAC outcome. We showed that the loss of both CD3-ε expression and CD3+ T cell number correlated with worse OS in EAC. The gene related to anergy in lymphocytes isoform 1 (GRAIL1), which is the prominent isoform in EACs, degraded (ε, γ, δ) CD3s and inactivated T cells. In contrast, isoform 2 (GRAIL2), which is reduced in EACs, stabilized CD3s. Further, GRAIL1-mediated CD3 degradation was facilitated by interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15), a ubiquitin-like protein. Consequently, the overexpression of a ligase-dead GRAIL1, ISG15 knockdown, or the overexpression of a conjugation-defective ISG15-leucine-arginine-glycine-glycine mutant could increase CD3 levels. Together, we identified an ISG15/GRAIL1/mutant p53 amplification loop negatively influencing CD3 levels and T cell activity, thus promoting immunosuppression in EAC.
CEA-CD3 bispecific antibody cibisatamab with or without atezolizumab in patients with CEA-positive solid tumours: results of two multi-institutional Phase 1 trialsSegal, Melero, Moreno
et alNat Commun (2024) 15 (1), 4091
Abstract: Cibisatamab is a bispecific antibody-based construct targeting carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) on tumour cells and CD3 epsilon chain as a T-cell engager. Here we evaluated cibisatamab for advanced CEA-positive solid tumours in two open-label Phase 1 dose-escalation and -expansion studies: as a single agent with or without obinutuzumab in S1 (NCT02324257) and with atezolizumab in S2 (NCT02650713). Primary endpoints were safety, dose finding, and pharmacokinetics in S1; safety and dose finding in S2. Secondary endpoints were anti-tumour activity (including overall response rate, ORR) and pharmacodynamics in S1; anti-tumour activity, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics in S2. S1 and S2 enrolled a total of 149 and 228 patients, respectively. Grade ≥3 cibisatamab-related adverse events occurred in 36% of S1 and 49% of S2 patients. The ORR was 4% in S1 and 7% in S2. In S2, patients with microsatellite stable colorectal carcinoma (MSS-CRC) given flat doses of cibisatamab and atezolizumab demonstrated an ORR of 14%. In S1 and S2, 40% and 52% of patients, respectively, developed persistent anti-drug antibodies (ADAs). ADA appearance could be mitigated by obinutuzumab-pretreatment, with 8% of patients having persistent ADAs. Overall, cibisatamab warrants further exploration in immunotherapy combination strategies for MSS-CRC.© 2024. The Author(s).
A novel TCGA-validated programmed cell-death-related signature of ovarian cancerCai, Lin, Liu
et alBMC Cancer (2024) 24 (1), 515
Abstract: Ovarian cancer (OC) is a gynecological malignancy tumor with high recurrence and mortality rates. Programmed cell death (PCD) is an essential regulator in cancer metabolism, whose functions are still unknown in OC. Therefore, it is vital to determine the prognostic value and therapy response of PCD-related genes in OC.By mining The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) and Genecards databases, we constructed a prognostic PCD-related genes model and performed Kaplan-Meier (K-M) analysis and Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve for its predictive ability. A nomogram was created via Cox regression. We validated our model in train and test sets. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was applied to identify the expression of our model genes. Finally, we analyzed functional analysis, immune infiltration, genomic mutation, tumor mutational burden (TMB) and drug sensitivity of patients in low- and high-risk group based on median scores.A ten-PCD-related gene signature including protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 15 A (PPP1R15A), 8-oxoguanine-DNA glycosylase (OGG1), HECT and RLD domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase family member 1 (HERC1), Caspase-2.(CASP2), Caspase activity and apoptosis inhibitor 1(CAAP1), RB transcriptional corepressor 1(RB1), Z-DNA binding protein 1 (ZBP1), CD3-epsilon (CD3E), Clathrin heavy chain like 1(CLTCL1), and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (CEBPB) was constructed. Risk score performed well with good area under curve (AUC) (AUC3 - year =0.728, AUC5 - year = 0.730). The nomogram based on risk score has good performance in predicting the prognosis of OC patients (AUC1 - year =0.781, AUC3 - year =0.759, AUC5 - year = 0.670). Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) analysis showed that the erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog (ERBB) signaling pathway and focal adhesion were enriched in the high-risk group. Meanwhile, patients with high-risk scores had worse OS. In addition, patients with low-risk scores had higher immune-infiltrating cells and enhanced expression of checkpoints, programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1), indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO-1) and lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG3), and were more sensitive to A.443,654, GDC.0449, paclitaxel, gefitinib and cisplatin. Finally, qRT-PCR confirmed RB1, CAAP1, ZBP1, CEBPB and CLTCL1 over-expressed, while PPP1R15A, OGG1, CASP2, CD3E and HERC1 under-expressed in OC cell lines.Our model could precisely predict the prognosis, immune status and drug sensitivity of OC patients.© 2024. The Author(s).
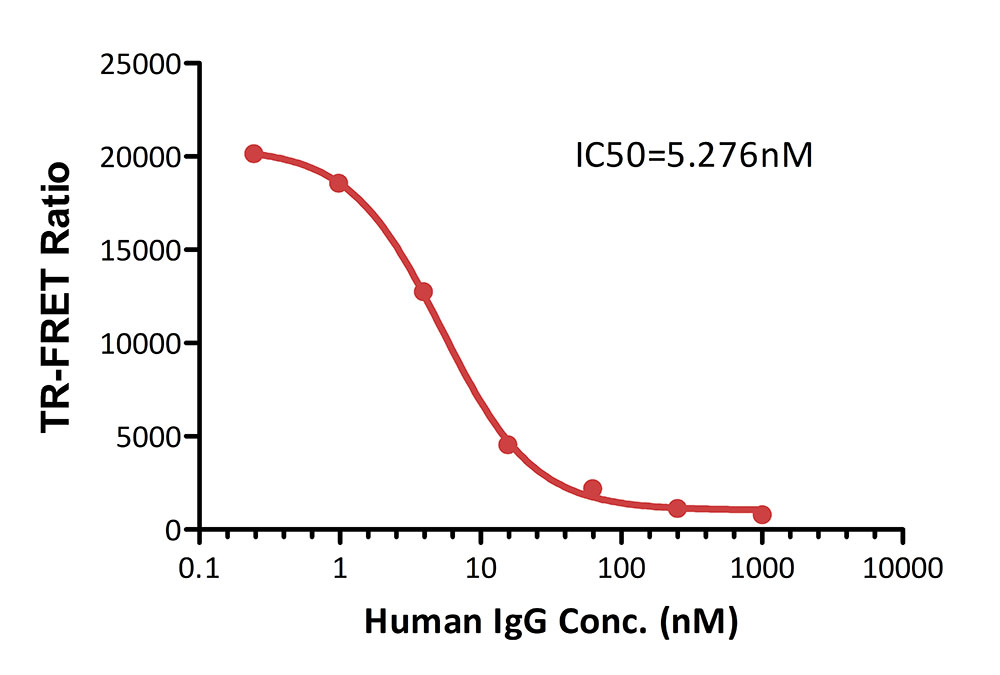
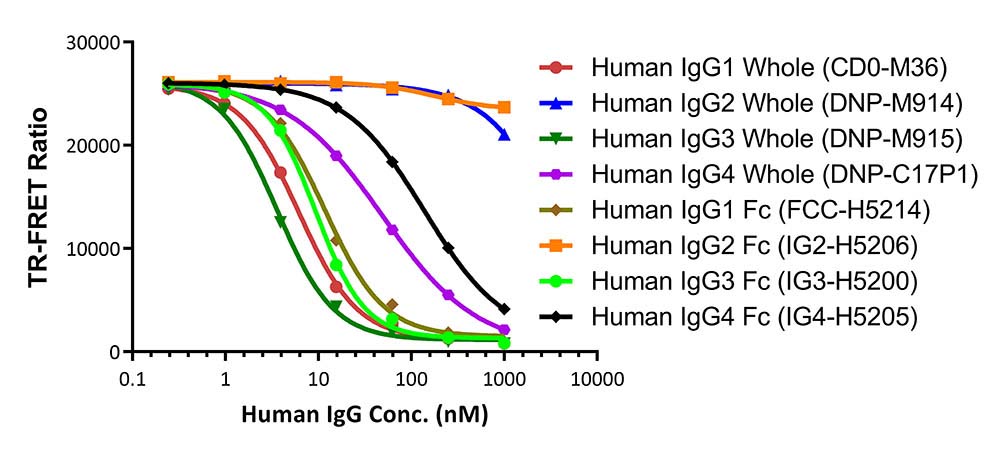
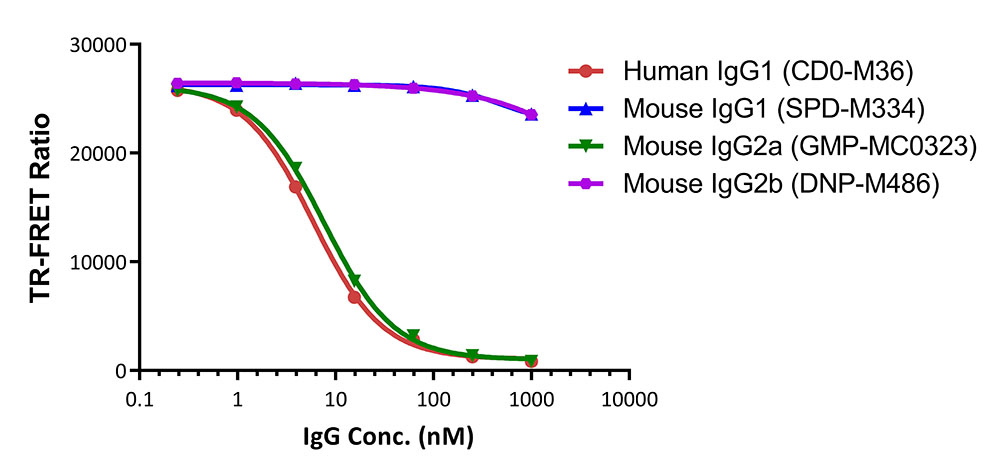
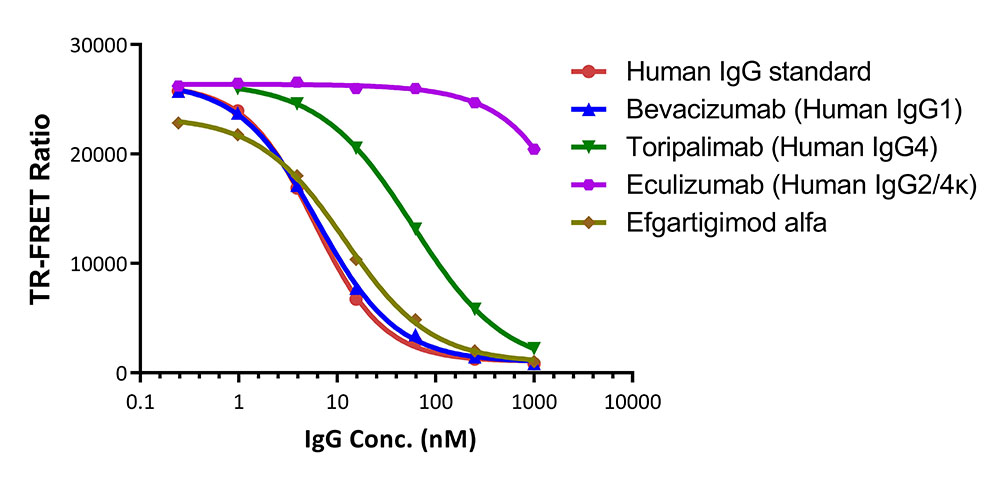























































 膜杰作
膜杰作 Star Staining
Star Staining















